As the world accelerates its transition toward cleaner mobility, electric vehicles (EVs) have become central to reducing carbon emissions and fossil fuel reliance. But at the heart of every EV lies its power source—the battery. These advanced energy storage systems are more than just components; they’re catalysts driving a technological and environmental revolution.
In recent years, innovations in battery chemistry, performance, and efficiency have made EVs more affordable, accessible, and sustainable. The evolution of this space is not only transforming how vehicles are powered, but also influencing global supply chains, manufacturing norms, and energy infrastructure.
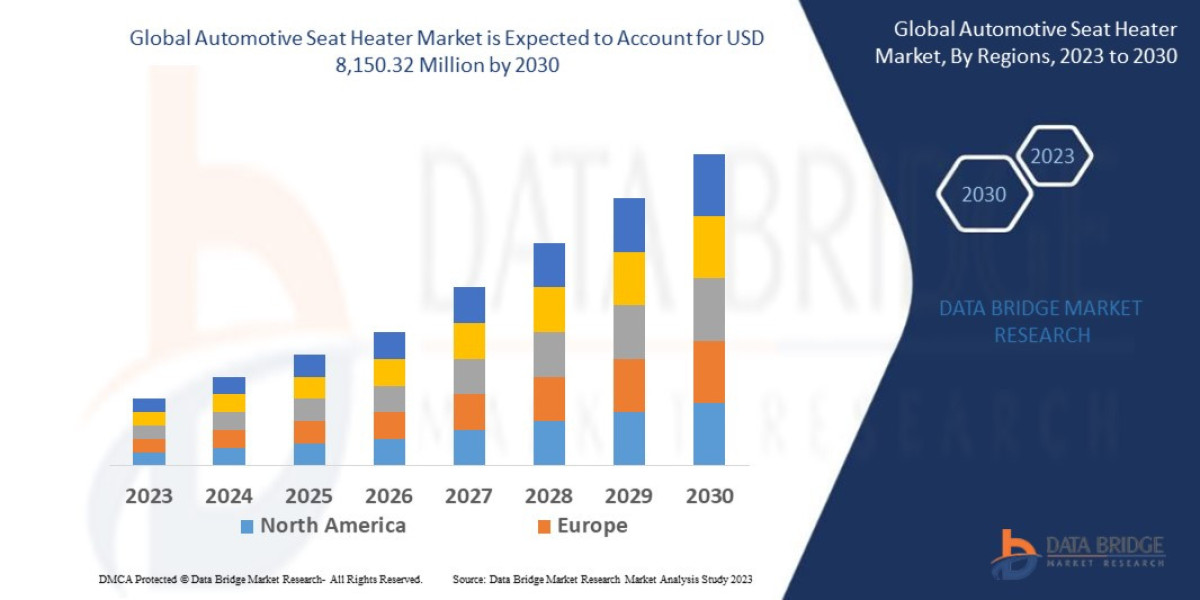
According to Marketintelo, “The global EV Battery Market size was valued at approximately USD 56.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 206.2 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.4% during the forecast period 2024–2032.”
What Makes EV Batteries So Critical?
Electric vehicle batteries are rechargeable energy storage units, typically based on lithium-ion chemistry. Their capacity, lifecycle, and efficiency determine the driving range, charging time, and overall vehicle performance. As governments across the globe push for electrification mandates, the demand for advanced EV batteries has surged dramatically.
Moreover, battery technology plays a pivotal role in making EVs competitive with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. With improved energy densities and reduced costs per kilowatt-hour (kWh), manufacturers are closing the gap between EVs and traditional cars.
Key Innovations Transforming Battery Technology
Several technical breakthroughs are shaping the next generation of EV batteries:
1. Solid-State Batteries
Unlike conventional liquid electrolyte batteries, solid-state versions promise higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety. Major automakers and tech companies are heavily investing in this emerging technology, which could potentially double EV range while minimizing fire risks.
2. Cobalt-Free Chemistries
The global EV battery supply chain has faced scrutiny over ethical and environmental concerns, particularly related to cobalt mining. In response, manufacturers are shifting toward cobalt-free chemistries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), offering a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative.
3. Fast-Charging Capabilities
Developments in battery management systems (BMS) and thermal regulation have significantly reduced charging times. Some next-gen batteries can now charge to 80% in under 15 minutes, addressing one of the most common EV adoption barriers: range anxiety.
Regional Trends and Competitive Landscape
As per Dataintelo’s analysis, “The regional distribution of the EV Battery Market reflects varying consumer preferences, market shares, and growth rates. For instance, Europe accounted for approximately 28.6% of the market share in 2024, generating close to USD 16.1 billion.”
Asia Pacific Leads in Manufacturing
Countries like China, South Korea, and Japan dominate the EV battery production landscape. China alone holds more than 70% of the global lithium-ion battery manufacturing capacity, thanks to strategic investments, favorable policies, and access to raw materials.
Europe’s Electrification Push
Driven by stringent emission norms and generous EV subsidies, European countries are rapidly adopting electric mobility. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are spearheading local battery manufacturing initiatives to reduce reliance on Asian imports.
North America’s Battery Corridor
With the U.S. government offering tax incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act and pushing for domestic production, several battery gigafactories are being set up across states like Nevada, Georgia, and Michigan. This strategic shift aims to secure supply chains and support local EV manufacturing.
Market Drivers Fueling EV Battery Demand
Government Regulations and Incentives
Global climate agreements and national policies are placing stricter limits on CO₂ emissions. Many countries have already announced timelines to phase out ICE vehicle sales. These regulatory measures are pushing both automakers and consumers toward EVs—creating direct demand for high-performance batteries.
Declining Battery Prices
Over the past decade, lithium-ion battery pack prices have dropped by over 85%. As costs continue to fall and economies of scale improve, EVs are becoming more competitively priced, especially in mass-market segments.
Surge in Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of EVs with solar and wind power is creating a dual-use opportunity for batteries—serving as both vehicle power and energy storage for homes and grids. This cross-sector synergy is making batteries a key player in broader energy transitions.
Challenges Confronting the EV Battery Market
Despite strong momentum, several challenges persist:
Raw Material Shortages
The mining and processing of lithium, nickel, and graphite—the primary elements in EV batteries—are concentrated in limited regions. Geopolitical instability and rising demand have led to price volatility and supply disruptions.
Recycling and Environmental Impact
As millions of EVs reach end-of-life, sustainable disposal and recycling of batteries are becoming crucial. Developing closed-loop battery recycling systems is essential to minimize environmental harm and recover valuable materials.
Infrastructure Gaps
Widespread EV adoption is constrained by inadequate charging infrastructure. Fast-charging stations, grid readiness, and standardized connectors must evolve in tandem with battery technology to ensure a seamless user experience.
Future Outlook: What's on the Horizon?
The next decade promises continued evolution in EV battery capabilities:
Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS): Subscription models for battery leasing and swapping are emerging, reducing upfront EV costs and improving accessibility.
AI-Driven Battery Management: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into battery systems for real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization.
Wireless Charging Integration: Inductive charging pads and dynamic charging lanes could redefine how EVs recharge—making the process frictionless and fully automated.
Second-Life Applications: Used EV batteries are being repurposed for stationary energy storage, giving them a second life in powering homes, businesses, and renewable energy setups.
Conclusion
The rise of the EV battery sector is not just a byproduct of the electric vehicle boom—it is the very backbone of the future of clean transportation. As breakthroughs in chemistry, infrastructure, and policy continue to unfold, EV batteries will only become more efficient, sustainable, and integral to global mobility.