Magnesium oxide, often referred to as magnesia, is a mineral compound with wide-ranging industrial applications. Known for its high melting point, thermal conductivity, and insulation properties, it plays a critical role in sectors such as construction, agriculture, steelmaking, and pharmaceuticals. Whether used as a refractory material in furnaces or a nutritional supplement in livestock feed, magnesium oxide has earned a place among essential compounds supporting modern infrastructure and health systems.
In recent years, global demand for magnesium oxide has surged due to its versatility and eco-friendliness. Its non-toxic nature and ability to resist high temperatures make it an ideal component in green technologies, including carbon capture systems and sustainable building materials. As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and environmental compliance, magnesium oxide is positioned as a key solution.
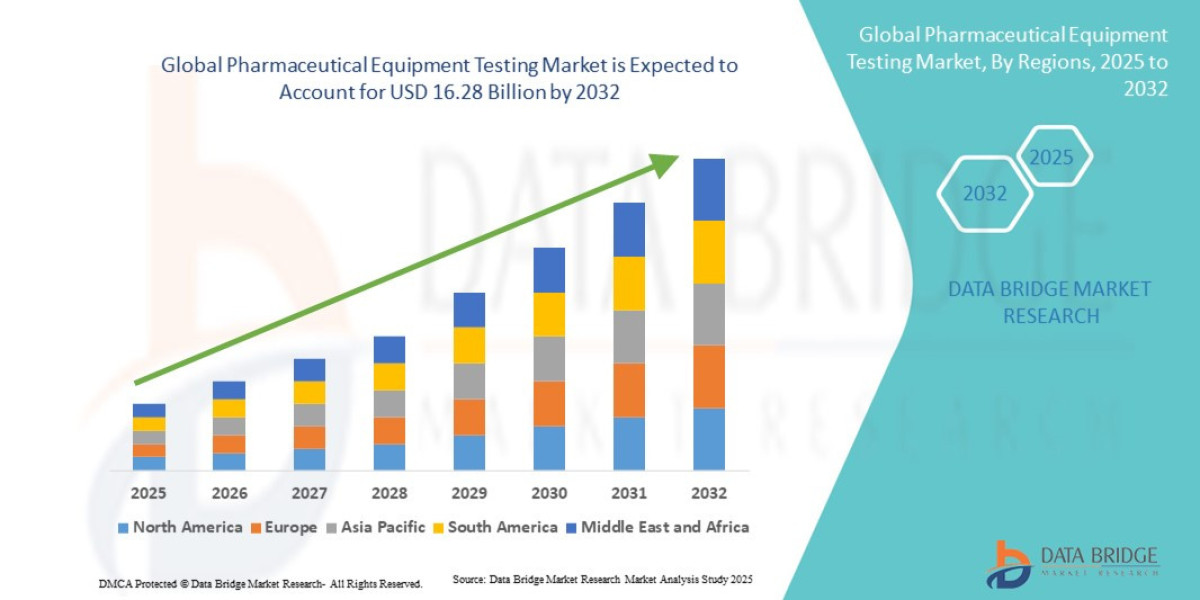
According to Marketintelo, “The global Magnesium Oxide Market size was valued at approximately USD 6.9 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 10.7 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% during the forecast period 2024–2032.”
Read Full Research Study – https://marketintelo.com/report/magnesium-oxide-market
One of the most prominent uses of magnesium oxide is in the production of refractory materials. These are heat-resistant substances that maintain structural integrity under extreme temperatures, essential in industries such as steel, glass, and ceramics. Magnesia-based bricks are especially valued in steelmaking, where they line furnaces and converters to protect infrastructure and extend operational life. The growing demand for steel from developing economies is consequently fueling magnesium oxide consumption.
As per Dataintelo’s analysis, “The regional distribution of the Magnesium Oxide Market reflects varying consumer preferences, market shares, and growth rates. For instance, Europe accounted for approximately 28% of the market share in 2024, generating close to USD 1.9 billion.”
Read Full Research Study – https://dataintelo.com/report/global-magnesium-oxide-market
Europe's significant share is driven by its strong focus on renewable energy, sustainable construction, and chemical manufacturing. Magnesium oxide is widely used in flue gas desulfurization units in power plants, where it helps capture sulfur dioxide emissions. Its application in magnesium cement for eco-friendly building materials is also expanding across European green construction projects.
In Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, the surge in manufacturing, metallurgy, and infrastructure development is driving substantial demand. China, with its extensive refractory and cement industries, remains one of the largest consumers and producers of magnesium oxide. The region's focus on rapid urbanization and expanding industrial capacity keeps demand on a steady upward trajectory.
Meanwhile, North America is experiencing growing utilization in the agricultural and environmental sectors. In farming, magnesium oxide is used to improve soil quality and balance pH levels, contributing to higher crop yields. It’s also added to animal feed as a magnesium supplement, especially for dairy cattle. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s increasing regulation of emissions and waste disposal is boosting demand for magnesia-based environmental solutions.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries represent another important end-use category. Magnesium oxide is commonly formulated into supplements for its laxative properties and as a source of dietary magnesium, particularly in regions where magnesium deficiency is prevalent. Its use in over-the-counter medications ensures a consistent demand regardless of economic cycles.
Construction materials are evolving as well. Magnesium oxide boards, often called MgO boards, are gaining traction as fire-resistant, mold-resistant alternatives to gypsum drywall. Lightweight and durable, MgO boards are increasingly used in modular construction, prefab housing, and buildings located in moisture-prone regions. Their adoption is supported by growing concerns about building resilience and fire safety.
Environmental applications of magnesium oxide continue to grow. Its alkaline properties make it useful for treating wastewater and industrial effluents by neutralizing acidity and removing heavy metals. In carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, magnesium oxide is being explored for its potential to sequester carbon dioxide through mineralization processes—a promising tool in the fight against climate change.
Despite its many advantages, challenges remain. The extraction and calcination processes required to produce magnesium oxide are energy-intensive and contribute to carbon emissions. Additionally, the cost and availability of high-purity magnesite ores—used as raw material—can fluctuate due to geopolitical factors and export restrictions, especially in China, a major supplier.
Innovations in production technology are attempting to mitigate these drawbacks. Research into low-temperature synthesis methods and use of alternative feedstocks, such as seawater-derived magnesium hydroxide, could help lower emissions and diversify supply sources. These efforts align with broader trends toward circular economy practices and resource efficiency.
From a competitive perspective, key market players such as RHI Magnesita, Martin Marietta, Premier Magnesia, and Grecian Magnesite are actively investing in research and capacity expansion. Strategic partnerships and mergers are also reshaping the landscape, helping companies secure raw materials, enter new geographic markets, and strengthen supply chains.
Digitization and automation are being adopted in magnesia manufacturing plants to improve quality control, reduce downtime, and optimize energy use. AI-powered analytics and IoT sensors allow producers to fine-tune calcination processes and predict maintenance needs, enhancing both productivity and sustainability.
Geopolitical dynamics are also influencing the market. Countries are increasingly focused on securing domestic supplies of essential minerals, including magnesium compounds, in response to trade uncertainties and supply chain vulnerabilities exposed during recent global disruptions. Policies supporting local extraction, processing, and innovation are gaining traction.
In terms of regulations, the use of magnesium oxide in food and pharma sectors requires strict compliance with safety and purity standards. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA, European Medicines Agency, and Codex Alimentarius provide frameworks that ensure magnesia-based products meet health and environmental guidelines. These rules contribute to consistent product quality but can also raise production costs.
Looking ahead, magnesium oxide's role is expected to expand alongside technological advancements and changing regulatory priorities. As industries pursue decarbonization and efficiency, the demand for high-performance, sustainable materials like magnesia will only intensify. Its integration into next-gen materials, eco-friendly construction, and emissions control positions magnesium oxide as a critical enabler of industrial transformation.
In conclusion, magnesium oxide is far more than a basic industrial compound—it is a multifunctional material that supports global progress in steelmaking, environmental protection, agriculture, construction, and healthcare. As production technologies improve and demand continues to grow, the magnesium oxide market is entering a new phase of strategic importance across multiple economies and value chains.