Bio plastic packaging is increasingly becoming a key alternative to conventional plastics, offering environmentally friendly options for various sectors. These materials, derived from renewable sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and cellulose, aim to reduce carbon footprints and enhance biodegradability. Their adoption aligns with rising consumer awareness and regulatory pressure to minimize plastic waste and promote circular economy practices.
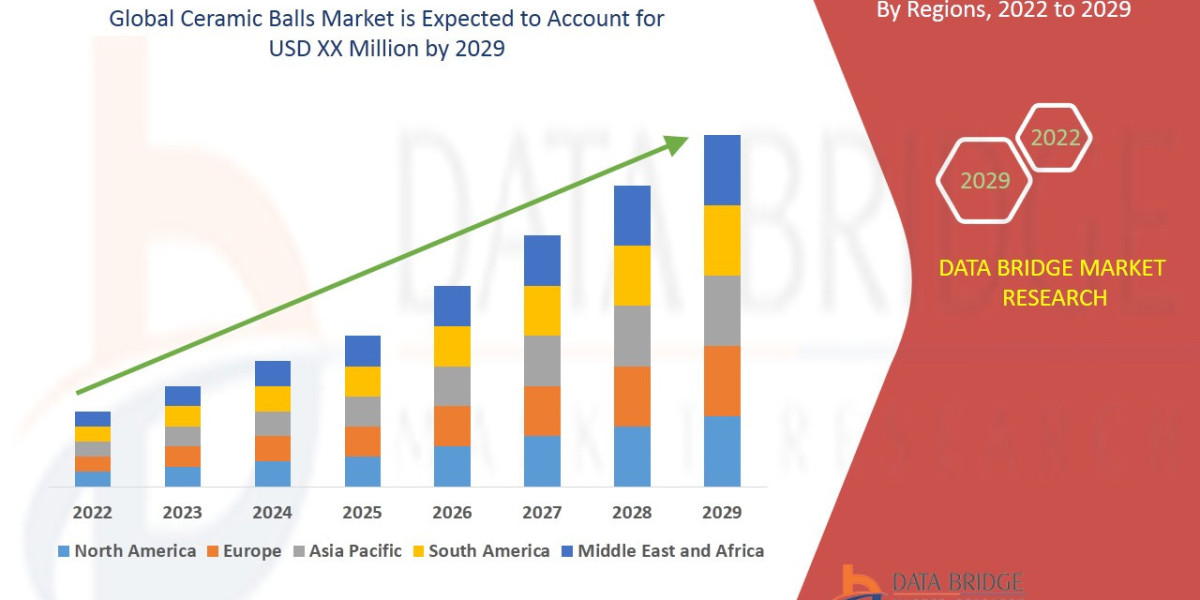
According to Marketintelo, “The global Bio Plastic Packaging size was valued at approximately USD 9.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 17.8 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% during the forecast period 2024–2032.”
Read Full Research Study – “https://marketintelo.com/report/bio-plastic-packaging-market”
Advantages Driving Adoption
Bio plastic packaging offers multiple benefits over traditional plastics. Biodegradability and compostability reduce landfill accumulation and environmental pollution. Additionally, bio plastics often require less energy to produce, supporting sustainability objectives.
Functionality and versatility make these materials suitable for food packaging, beverage containers, healthcare applications, and consumer goods. They provide protective qualities, durability, and compatibility with modern manufacturing techniques while aligning with eco-conscious branding.
Types of Bio Plastic Packaging
Bio plastic packaging can be broadly categorized into polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), starch-based plastics, and cellulose-based materials. PLA is widely used in food and beverage packaging due to its clarity and strength. PHA offers full biodegradability and is suited for compostable applications. Starch-based and cellulose materials provide flexible, lightweight alternatives for bags, wraps, and disposable containers.
Each type presents unique mechanical properties and environmental benefits, allowing manufacturers to choose materials based on specific application requirements and sustainability targets.
Regional Insights and Demand Patterns
As per Dataintelo’s analysis, “The regional distribution of the Bio Plastic Packaging reflects varying consumer preferences, market shares, and growth rates. For instance, Europe accounted for approximately 37% of the market share in 2024, generating close to USD 3.52 billion.”
Read Full Research Study – “https://dataintelo.com/report/bio-plastic-packaging-market”
Europe leads adoption due to stringent environmental regulations, strong consumer awareness, and incentives for sustainable packaging. North America follows, driven by corporate sustainability initiatives and regulatory compliance. Asia-Pacific is witnessing rapid expansion as emerging economies focus on eco-friendly alternatives amid increasing plastic waste concerns.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and affordability of bio plastic packaging. Improvements in polymer formulations, blending techniques, and extrusion processes enable better mechanical properties, heat resistance, and barrier functionality.
Innovations such as antimicrobial coatings, high-clarity films, and multi-layer bio plastic composites expand applications across food, healthcare, and consumer products. Research continues to focus on reducing production costs while increasing material efficiency and recyclability.
Environmental and Consumer Impact
Bio plastic packaging significantly contributes to environmental conservation by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Compostable and biodegradable variants minimize landfill accumulation, supporting waste management initiatives and circular economy strategies.
Consumer awareness regarding eco-friendly packaging has grown substantially. Many buyers now prioritize products with sustainable packaging, influencing brand strategies and driving demand for bio-based alternatives across retail and e-commerce sectors.
Regulatory Influence and Compliance
Government regulations and policies are essential drivers for bio plastic adoption. Restrictions on single-use plastics, plastic bag bans, and mandates for recyclable or compostable packaging encourage manufacturers to integrate bio-based materials. Certification standards such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 validate compostability and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Regulatory frameworks also support innovation through funding, research grants, and tax incentives, promoting the development of next-generation bio plastic materials and production technologies.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite advantages, challenges remain in bio plastic packaging adoption. Higher production costs compared to conventional plastics, limited mechanical strength for certain applications, and insufficient recycling infrastructure pose obstacles. Consumer confusion regarding biodegradability and compostability labeling can also affect acceptance.
Overcoming these challenges requires investment in R&D, process optimization, and public awareness campaigns. Collaboration between manufacturers, regulatory authorities, and supply chain stakeholders is vital to ensure consistent quality and scalability.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
The future of bio plastic packaging lies in expanding applications, improving material properties, and integrating circular economy principles. Innovations in biodegradable composites, reusable packaging, and hybrid solutions that combine bio plastics with conventional polymers will enhance performance and accessibility.
Increasing urbanization, e-commerce expansion, and sustainability-conscious consumer behavior provide opportunities for wider adoption. Partnerships between packaging manufacturers, brands, and waste management providers will help create comprehensive solutions for eco-friendly packaging and responsible disposal.
Conclusion
Bio plastic packaging represents a shift toward sustainable, environmentally responsible solutions that balance performance with ecological benefits. With rising regulatory pressure, consumer demand, and technological advancements, these materials are redefining packaging standards globally.
Regional adoption patterns, material innovations, and functional versatility collectively shape the landscape, ensuring bio plastic packaging remains a practical and eco-conscious alternative. As manufacturers continue to optimize production, enhance properties, and educate consumers, bio plastics are set to play a critical role in reducing plastic pollution and supporting a sustainable future.