In an era where digital security is becoming just as critical as physical safety, biometric door locks are rapidly gaining attention. Unlike traditional mechanical locks and PIN-based systems, these locks integrate fingerprint recognition, facial scanning, and sometimes iris authentication, offering a higher level of protection. With rising concerns over burglary, unauthorized access, and the need for smarter living solutions, biometric locks are finding applications in homes, offices, hotels, and government facilities.
According to Marketintelo, “The global Biometric Door Lock size was valued at approximately USD 2.8 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.9 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.5% during the forecast period 2024–2032.”
Read Full Research Study – “https://marketintelo.com/report/biometric-door-lock-market”
What Makes Biometric Locks Different?
The key differentiator of biometric locks lies in their authentication process. Instead of relying on keys or codes that can be stolen, lost, or duplicated, these systems use unique biological identifiers. Fingerprint-based locks remain the most common type, but facial recognition technology is steadily expanding due to its hands-free convenience. Some high-security environments are also adopting iris-based verification, which is difficult to replicate or forge.
Apart from security, biometric locks enhance convenience. Users no longer need to carry keys or remember complex passwords. In commercial spaces, administrators can control and monitor access more efficiently, integrating with digital logs that track who enters and exits at specific times. This capability is especially valuable for offices, co-working hubs, and institutions where security and accountability are priorities.
Market Drivers Behind Adoption
Several factors are fueling the adoption of biometric door locks. First, the global surge in urbanization has amplified the demand for modern housing equipped with smart home technologies. Biometric locks align seamlessly with this trend, complementing IoT-enabled devices and home automation systems.
Second, the rising number of security breaches and theft cases has pushed both consumers and businesses to explore stronger access control solutions. The hospitality industry, for example, is shifting toward biometric-enabled room access to enhance guest safety and convenience. Similarly, corporate offices are deploying biometric authentication to safeguard sensitive areas and digital data centers.
Third, advancements in sensor technology and declining hardware costs have made biometric locks more affordable. Manufacturers are now offering products that integrate with smartphones, cloud storage, and AI-powered analytics, broadening the appeal to tech-savvy users and organizations.
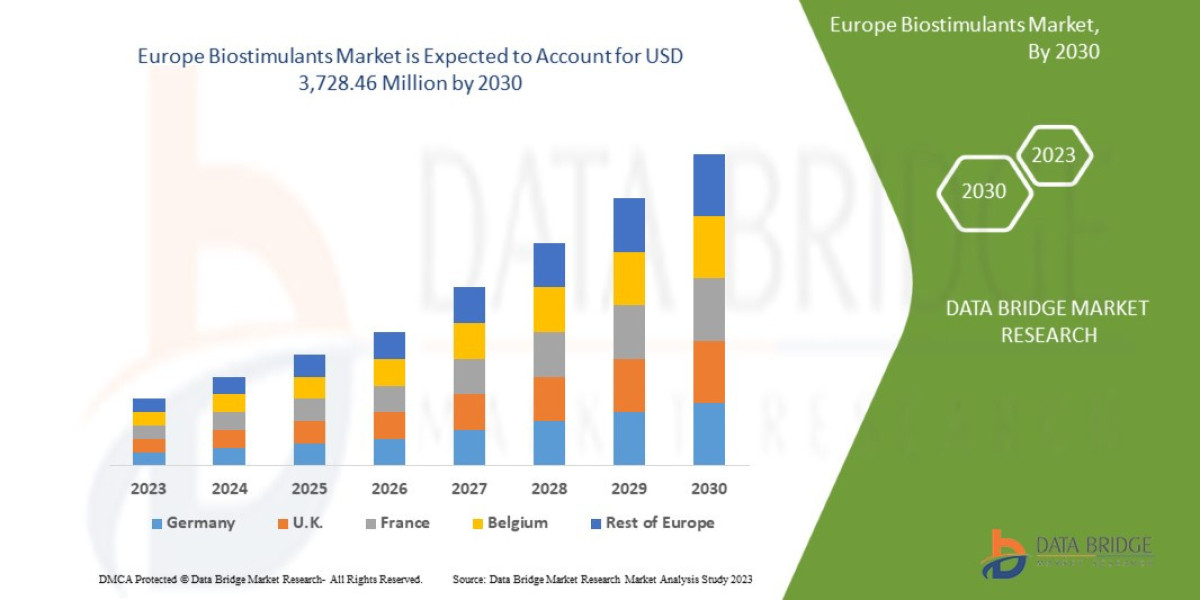
As per Dataintelo’s analysis, “The regional distribution of the Biometric Door Lock reflects varying consumer preferences, market shares, and growth rates. For instance, Europe accounted for approximately 28% of the market share in 2024, generating close to USD 784 million.”
Read Full Research Study – “https://dataintelo.com/report/biometric-door-lock-market”
Regional Highlights
North America remains a stronghold for biometric door locks, primarily driven by high consumer awareness and the adoption of smart home ecosystems. The United States, with its expanding base of home automation users, continues to dominate regional demand.
Europe, as highlighted, represents a significant share, with governments implementing stricter building safety codes and consumers investing in modern security systems. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are spearheading adoption, particularly in residential and hospitality applications.
Asia-Pacific, however, is expected to be the fastest-growing region. With rapid urban expansion, a booming middle-class population, and increasing disposable incomes, countries like China, India, and South Korea are embracing biometric security solutions. The integration of smart locks into large-scale apartment complexes and commercial buildings is a particularly strong driver here.
Key Applications Across Sectors
Biometric door locks are not confined to homes. Their applications span a wide spectrum:
Residential: Homeowners prioritize convenience and security, with fingerprint locks being the most popular choice.
Commercial: Offices and enterprises integrate biometric systems for employee authentication and secure data rooms.
Hospitality: Hotels enhance guest experience with keyless biometric access, reducing risks tied to lost or stolen keycards.
Government and Defense: Sensitive facilities rely on multi-modal biometric authentication, combining fingerprint, face, and iris scans.
Educational Institutions: Universities and schools use biometric locks to restrict access to labs, libraries, and administrative offices.
Challenges in the Adoption of Biometric Locks
While the benefits are clear, certain challenges remain. High upfront installation costs can deter price-sensitive consumers, especially in developing markets. Technical issues, such as fingerprint mismatches or sensor malfunctions, can also affect reliability. Additionally, privacy concerns around biometric data storage continue to spark debates.
Manufacturers are addressing these issues by enhancing sensor accuracy, providing hybrid systems that support both biometric and PIN access, and adopting secure encryption methods for data handling. Cloud-based solutions with multi-layer authentication are further mitigating privacy-related risks.
Future Prospects for Biometric Security
Looking ahead, the biometric door lock landscape is set for significant transformation. AI-driven facial recognition is expected to gain momentum, offering enhanced accuracy under varying lighting conditions and user appearances. The integration of biometric locks into broader smart city infrastructure may also become a reality, linking residential complexes, transportation hubs, and public institutions under unified access control systems.
Another promising direction lies in multi-modal authentication, where biometric locks combine fingerprint, face, and voice recognition for added layers of security. This approach could redefine high-security access in sectors like defense, banking, and healthcare.
Sustainability is also entering the conversation, with manufacturers exploring energy-efficient biometric locks powered by renewable energy sources or low-power consumption chips. Combined with mobile app integration and remote access features, these innovations are expected to widen consumer acceptance globally.
Conclusion
Biometric door locks represent a shift from traditional keys and codes toward personalized, technology-driven security. As smart living becomes mainstream, their role in residential, commercial, and institutional spaces will only deepen. Despite challenges such as cost and data privacy, ongoing advancements in AI, IoT integration, and affordability are positioning biometric locks as the cornerstone of next-generation security.
With urbanization, smart homes, and security awareness converging, biometric door locks are no longer futuristic—they are becoming an essential element of modern safety. Their adoption across regions highlights both current demand and future potential, making them a vital part of the global security ecosystem.