Executive Summary
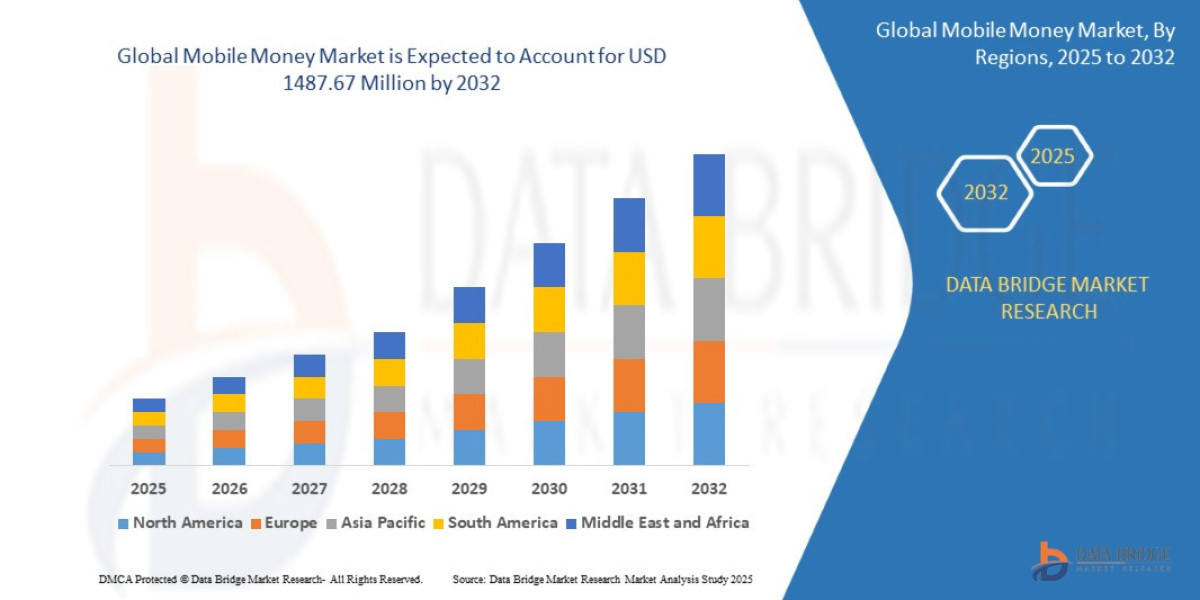
- The global mobile money market was valued at USD 139.73 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1487.67 million by 2032
- During the forecast period of 2025 to 2032 the market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 34.40%,
Market Overview
The Mobile Money Market is defined by services delivered primarily via a mobile phone, typically through a dedicated agent network, and often leveraging USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data) technology, though feature phone and smartphone apps are increasingly prevalent. These services are often operated by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) or specialized Fintechs, regulated under specific e-money or payments licenses.
Key Segments by Service Type
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transfers (Dominant Segment): Money sent between individual users, forming the foundational utility of mobile money.
Cash-in/Cash-out (CICO): The physical deposit and withdrawal of funds via authorized agents, maintaining the critical link to the physical economy.
Merchant Payments (M-Commerce): Payments made to businesses for goods and services. This is a high-growth segment, essential for digitizing local economies.
Bulk Payments: Used by governments and NGOs for salary disbursements, social welfare payments, and aid distribution.
Value-Added Services (VAS): Includes utility bill payments, international remittances, micro-insurance, and digital savings/credit products.
Key Segments by Technology
USSD-based Services: Crucial for reaching users with basic feature phones, particularly in rural areas with low internet penetration (e.g., M-Pesa).
App-based Services: Leveraging smartphone capabilities for enhanced user experience, advanced security features, and integration with third-party applications.
Drivers and Current Dynamics
Core Market Drivers:
Banking the Unbanked: Mobile money provides the only viable financial access point for hundreds of millions in emerging markets where bank branch infrastructure is non-existent.
High Mobile Penetration: Global mobile phone ownership, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, far exceeds traditional bank account ownership.
Low Cost Structure: The agent network model is far cheaper to operate than traditional bank branches, allowing services to be delivered affordably to low-income customers.
Government and Regulatory Support: Policy initiatives aimed at boosting financial inclusion often favor and promote the mobile money ecosystem.
Current Dynamics: The market is shifting from an MNO-centric model to one of interoperability and platformization. Operators are increasingly forced or choosing to open their networks to competing wallets and banks, making the customer experience more seamless but intensifying competition on service quality and product innovation.
Market Size & Forecast
- The global mobile money market was valued at USD 139.73 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1487.67 million by 2032
- During the forecast period of 2025 to 2032 the market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 34.40%,
For More Information visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-mobile-money-market
Key Trends & Innovations
Innovation is focused on leveraging data, integrating services, and enhancing the customer journey.
1. Interoperability and Open APIs
The trend toward full interoperability (allowing users to move funds easily between different mobile money providers, banks, and payment switches) is a crucial industry shift. Driven by regulation and competition, open APIs allow third-party developers (Fintechs) to build new services directly atop the mobile money rails, dramatically increasing ecosystem utility.
2. Digital Credit and Lending Automation
Mobile money providers sit on a wealth of transaction data, allowing them to build sophisticated credit scoring models for the unbanked. Automated, short-term, instant digital loans (e.g., M-Shwari) are generating significant revenue and providing essential liquidity to millions of micro-entrepreneurs.
3. Transition to Agent-less Digital Services
While the CICO agent network remains vital, service models are evolving to reduce reliance on the physical agent. This includes:
QR Code Payments: Facilitating easier, low-cost merchant transactions.
Near-Field Communication (NFC): Enabling tap-and-pay functionality where infrastructure allows.
IoT Integration: Using mobile money rails for smart metering, utility payments, and solar financing (Pay-As-You-Go models).
4. Regulatory Sandboxes and CBDCs
Regulators are increasingly using Fintech sandboxes to test and scale new mobile money models safely. Furthermore, the development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) is being actively considered in many mobile money-dominant nations (e.g., Nigeria’s eNaira), posing both a competitive threat and a potential new layer of infrastructure for mobile money providers.
Competitive Landscape
The market is fiercely competitive, largely between telecommunication giants and specialized payment platforms, with traditional banks often struggling to keep pace.
Major Players and Strategic Strategies
Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) (e.g., Safaricom/Vodacom [M-Pesa], Orange, MTN): Their strategy is Ecosystem and Agent Network Dominance. They leverage their massive subscriber base and existing distribution networks (airtime agents) to acquire users and maintain the widest physical CICO network. Their primary goal is to monetize airtime revenue and retain subscribers by offering sticky financial services.
Fintech Platforms and Super-Apps (e.g., Paytm, Gojek/GoPay, Chipper Cash): Their strategy is Service Aggregation and Interoperability. They focus on building integrated platforms that offer a multitude of services (payments, transport, food delivery) and connect to multiple banks and wallets, competing primarily on user experience and convenience.
Traditional Banks (Tier-2 Strategy): Many banks initially viewed mobile money as a threat but have now pivoted to a Partnership and Platform Strategy. They often partner with MNOs or Fintechs to offer their lending and savings products via the mobile money rails, leveraging the mobile money user base without incurring the cost of building their own agent network.
The core competitive battle is shifting from basic user acquisition to user engagement and the cross-selling of high-margin financial products.
Regional Insights
While mobile money is a global phenomenon, its maturity and deployment models are highly distinct across key geographies.
Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) (The Pioneer and Leader)
Performance: The global benchmark. SSA is defined by high CICO dependency, USSD dominance, and MNO-led systems. Kenya (M-Pesa) remains the most mature ecosystem globally. Transaction values are immense, driving a significant percentage of national GDP in countries like Kenya and Ghana.
Opportunity: Deepening financial services (credit, insurance) and expanding M-Commerce into rural and informal economies. Interoperability is the current regulatory focus to boost competition.
Asia-Pacific (APAC) (High Growth and Super-Apps)
Performance: Highly fragmented but rapidly growing. The market is defined by a fierce battle between specialized payments players (e.g., Paytm, Alipay, GoPay) and high smartphone penetration leading to app-based dominance.
Opportunity: Massive scale in countries like India (UPI rail) and Indonesia, focusing on integrating payments with ride-hailing, e-commerce, and food delivery to create "super-app" ecosystems.
Latin America (LatAm) (Emerging and Banking-Led)
Performance: Historically dominated by traditional banking structures, but mobile money and digital banking (Neobanks) are rapidly catching up, targeting populations underserved by expensive traditional institutions. Adoption is typically app-based.
Opportunity: High potential for cross-border remittances and digital asset integration, leveraging strong consumer adoption of digital technologies.
Challenges & Risks
While growth is strong, the mobile money ecosystem faces significant structural and trust-related challenges.
1. Regulatory Fragmentation and Compliance
Mobile money operates under a patchwork of national regulations. Compliance across multiple countries is complex and expensive, particularly concerning AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements, which are often difficult to enforce effectively with low-documentation customers.
2. Agent Network Management and Liquidity
The agent network is the market's backbone, but managing the liquidity of thousands of agents (ensuring they have enough physical cash for CICO transactions) is a constant operational challenge. Fraud, inconsistent service quality, and agent attrition are persistent risks.
3. Cybersecurity and Consumer Trust
As mobile money replaces cash, it becomes a prime target for cyber threats and phishing scams. Maintaining customer trust, particularly among digitally illiterate users, is paramount. Perceptions of inadequate protection against fraud can quickly undermine adoption.
4. Over-Indebtedness from Digital Credit
The speed and ease of obtaining automated digital loans, particularly when multiple competing providers target the same customer, can lead to over-indebtedness among low-income users, drawing sharp regulatory scrutiny and potentially damaging the reputation of the financial inclusion movement.
Opportunities & Strategic Recommendations
The future of mobile money lies in leveraging its massive data footprint and ubiquitous distribution network to become a fully fledged financial services platform.
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
Platformization and API Monetization (MNOs): MNOs must transform their mobile money service into a true open platform, offering APIs that allow Fintechs to integrate and innovate. This shifts the revenue model from transaction fees alone to data monetization, platform fees, and enhanced value-added service commissions.
Focus on M-Commerce and Digitalization of MSMEs (Fintechs): The highest potential growth is in digitizing the small and micro-enterprise (MSME) sector. Strategic deployment of QR code solutions, low-cost POS terminals, and inventory management tools integrated with mobile payments will unlock significant transaction volumes.
Cross-Border Expansion via Blockchain (Startups): Smaller operators and new entrants should focus on the lucrative international remittance corridor, utilizing faster, cheaper underlying technologies like blockchain or specialized global payment networks to bypass expensive traditional correspondent banking rails.
Develop Data-Driven Insurance and Savings (Banks/Operators): Utilize the vast transaction history to underwrite and auto-enroll customers into tailored, micro-insurance and micro-savings products (e.g., weather-indexed crop insurance, health savings accounts triggered by specific transactions). This improves customer loyalty and builds a sticky, high-margin revenue stream.
Browse More Reports:
Global Pediatric Imaging Market
Global Space Situational Awareness Market
Global Ophthalmology Small Molecule API Market
North America Wind Turbine Pitch System Market
Europe Diet and Nutrition Apps Market
Global Bunyavirus Infections Market
Asia-Pacific Diet and Nutrition Apps Market
Global Bio preservation Market
Global Carded Blister Packaging Market
Global Heavy Duty Corrugated Packaging Market
Global Engine and Transmission Thermal Systems Market
Global Dental Practice Management Software Market
Global Cigarette Butt Market
Global Sachet Packaging Market
Global Compostable Toothbrush Market
Global Noise Source Mapping Market
Global Ballistic Protection Bulletproof Glass Market
Global Hair Relaxer Market
Global Fortified Breakfast Cereals Market
Global Robotic Prosthetics Market
Global Micro and Nano Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Market
Global Fiber Drums Market
Europe Plant-Based Milk Market
North America Xylose Market
Global Laboratory Sterilizer Market
Global Aircraft Soft Goods Market
Global Duvet Covers Market
Middle East and Africa Hand Holes Market
Global Landau-Kleffner Treatment Market
Global Tralokinumab Market
Global LED Matrix Boards Outdoor LED Display Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com